Obesity and Infertility: Causes, Effects, and Solutions | Comprehensive Guide
Obesity has become a global health problem affecting nearly one third of world population, because of the changes in lifestyle and environment. According to WHO, the issue has evolved into an epidemic extent with over four million people dying because of complications of obesity.
What is obesity and how does it occur?
Obesity is defined as an abnormal accumulation of fat. When the BMI is over 25 and 30, it is considered overweight and obese, respectively. Obesity has become a pandemic because of our lifestyles and obesogenic environments such as calorie-dense food, sedentary lifestyle, changes in our biological clock due to stress, night shifts, and irregular meal consumption, etc., Both men and women are affected by this condition, however, women are at higher risk due to various factors such as sociocultural dynamics etc.
Obesity and its effect on male and female
Obesity has adverse effects on all systems and leads to a magnitude of complications such as cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, musculoskeletal disorders, and cancers, etc., Obesity can cause specific health conditions in males and females. Obesity-related problems in men are prostate cancer, erectile dysfunction, poor semen parameters, infertility, etc. Likewise, obesity in women is associated with anovulation, menstrual disorder, infertility, and cancers of the endometrium, ovary, and breast.
Obesity and male infertility
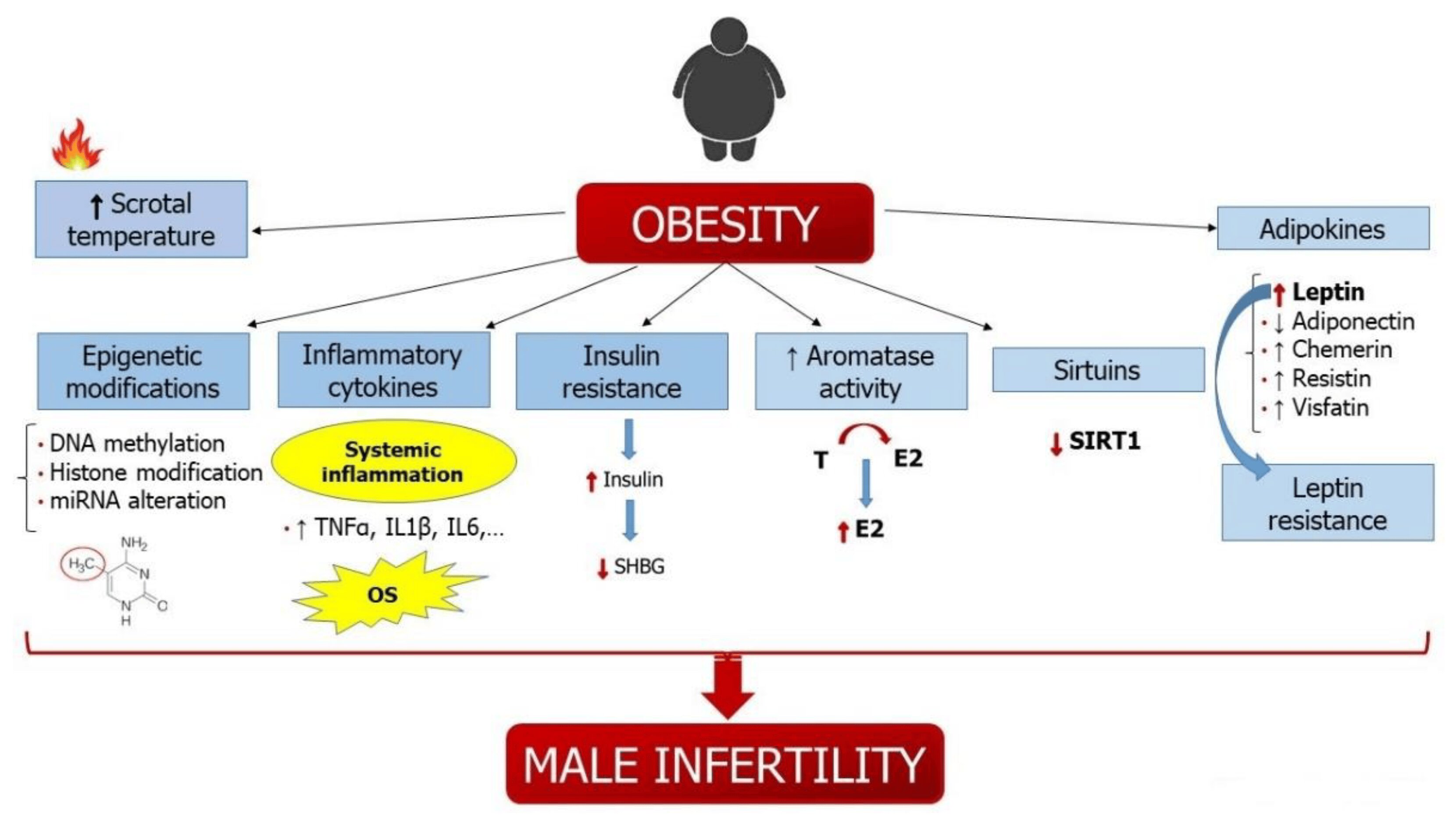
There is a complex association between obesity and male infertility. In contrast to normal individuals, obese people show the following features.
- Increased aromatase activity→ increased conversion of testosterone to oestradiol→ increased oestradiol→HPG axis inhibition→ Impair Testosterone production and spermatogenesis.
- Increased serum Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG)→ causes reduced testosterone
- Insulin resistance→hyperinsulinemia→ increases nuclear and mitochondrial DNA damage.
- Decreased Inhibin B→ indicate dysfunction of spermatogenesis.
- Testicular thermal stress increases-→ increases oxidative stress→sperm DNA fragmentation→ impairment of sperm parameters.
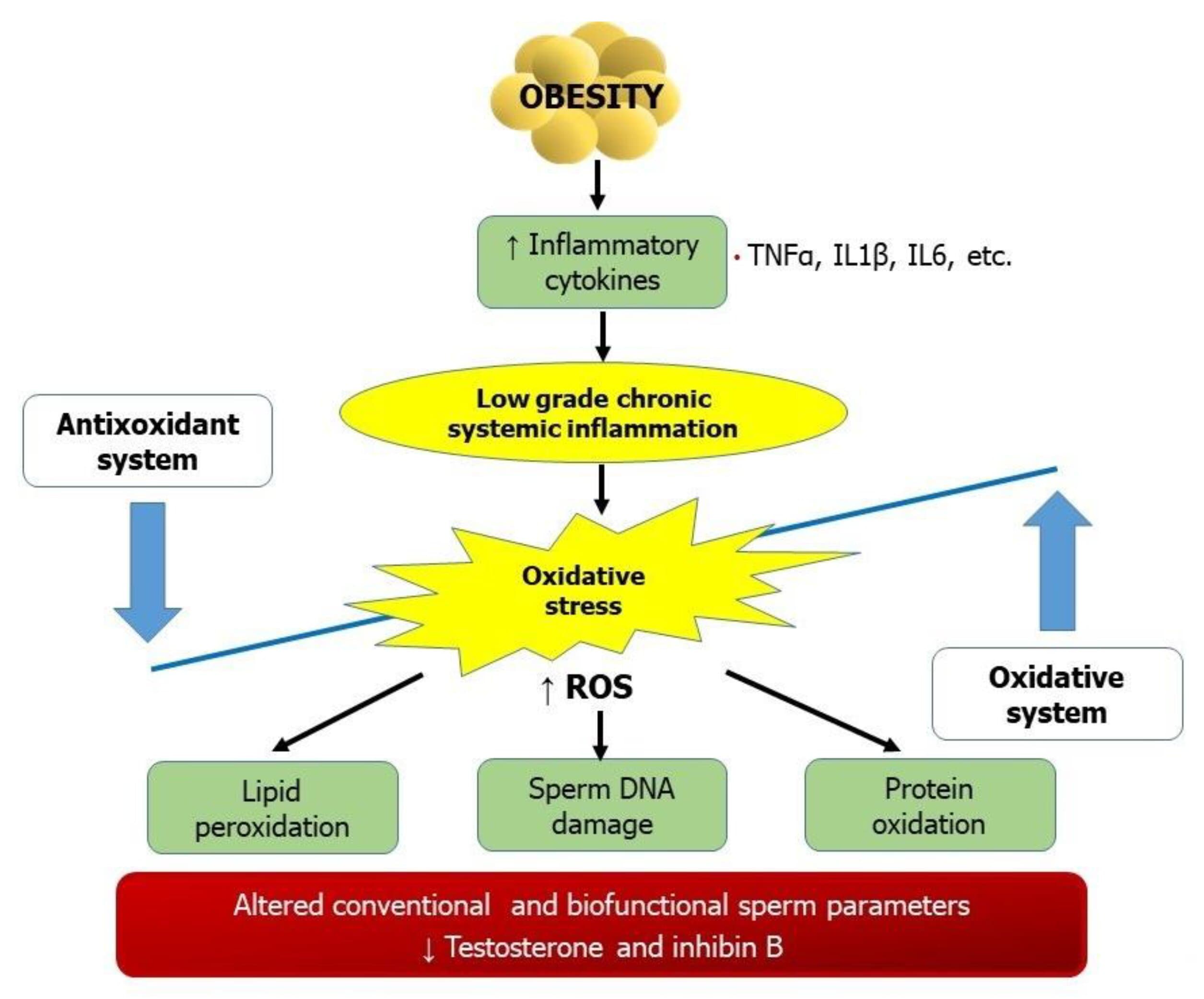
- Systemic oxidative stress and increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines which leads to a chronic inflammatory state. This chronic inflammatory state causes oxidative stress and increases Reactive oxygen species which at lower concentrations are essential for cellular functions but at higher concentrations, they damage DNA, proteins etc.
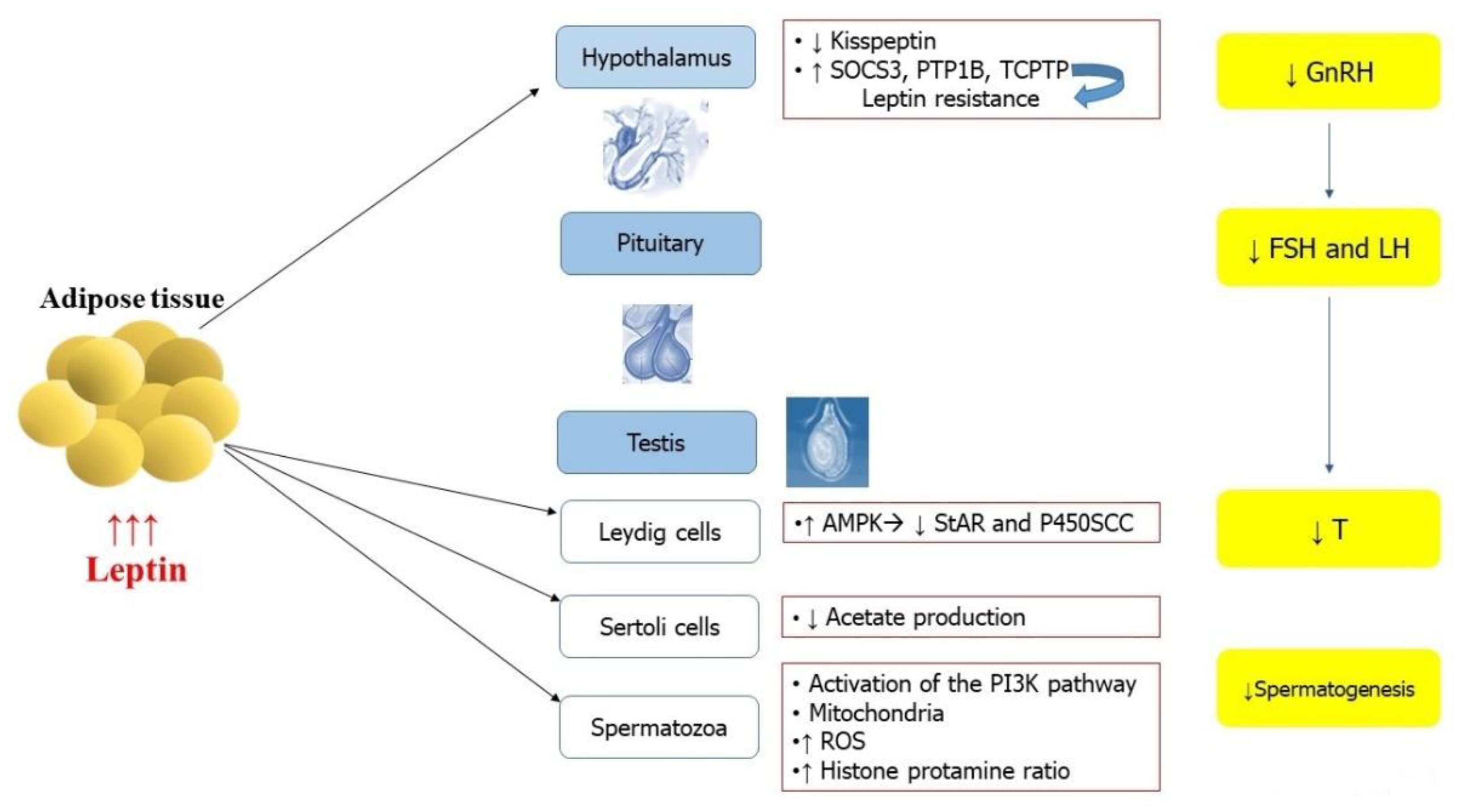
- Adipose tissue is not only a storehouse of energy but is also an endocrine organ with several hormones such as adipokines and immune molecules. Adipokines are cell signalling molecules produced by adipose tissue. Some notable adipokines are leptin, adiponectin, Interleukin- 6, etc., Excess of adipokines negatively affect fertility. It disrupts the Hypothalamic-pituitary axis which in turn decreases testosterone levels and spermatogenesis.
- Paternal obesity may negatively impact their children through epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs. Abnormal DNA methylation was associated with sperm DNA fragmentation and decreased pregnancy rates. Babies born to these fathers have altered DNA methylation themselves. These obesity-related epigenetic changes can be reversed by weight loss.
Obesity and female infertility
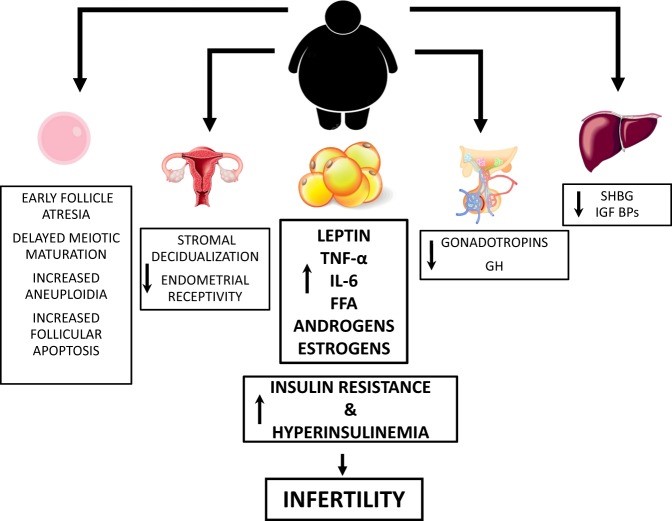
Obesity in women and its association with infertility is through multifaceted complex mechanisms. It causes infertility through ovarian and extra-ovarian mechanisms. Additionally, it affects the course and outcomes of IVF treatments. Obese people have hyperandrogenism and hyperestrogenism which affects their fertility by altering their ovarian and endometrial functions.
The following are numerous ways obesity affects female fertility.
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian Axis.
Leptin and other adipokines which are released from adipocytes are directly associated with the amount of fat present in the body. Increased Leptin affects the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis and there by affects ovarian function. Also, Leptin inhibits both granulosa and theca cells in the ovary which in turn affects steroidogenesis eventually affecting ovulation. - Insulin sensitivity
- Obesity is characterized by insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is nothing but decreased sensitivity of cells to insulin, which in turn causes compensatory hyperinsulinemia. Even though there is insulin resistance in many tissues, ovaries remain sensitive to it. Insulin has a stimulatory action on theca cells which produces androgens. Elevated levels of androgens cause premature follicular atresia and hence leading to anovulation.
- Hyperinsulinemia also causes→ reduced synthesis of SHBG in the liver→consequently increases free androgens→ thus causing hyperandrogenism which triggers overproduction of E1→ which in turn increases LH production→increased LH arrests earlier stage follicular growth.
- Dysregulation of Somatotropic axis
Obesity is characterized by decreased GH levels due to GHRH pathway and other pathways. GH is important for many functions of ovary such as stimulation of small follicle growth, luteinization, selection and development of dominant follicles etc., they are also involved in the preparation of endometrium in the uterus. - Quality of the oocyte.
- It is known that obesity affects the function of the ovary, however, recent studies have shown it is also involved in the impairment of oocyte quality. One reason could be because of altered mitochondrial activity in the oocyte because of obesity. In a study mitochondria from obese female mice showed 2-fold increased ROS.
- Endometrial receptivity
- Decreased stromal decidualization due to cytokines, other inflammatory markers, and ROS.
- Down-regulation of pathways needed for implantation.
- Reduced endometrial receptivity.
- Negative ART outcomes
Obesity is associated with the following in people undergoing ART treatments,- Need for higher doses of gonadotropins.
- Higher miscarriage rate
- Decreased pregnancy rate.
- Decreased live birth rate.
- Increased pregnancy related complications,such as
- Increased fetal malformations.
- Increased risk of IUD
- Neonatal complications
- PCOD
Obesity aggravates infertility in women with PCOS. The exact mechanism is not completely understood. However, some of the important factors contributing to infertility include the following,- Aggravates hyperandrogenism
- Insulin resistance
- Hyposomatotropinism
How to improve fertility in obese men and women
There is no most effective method, however the following options are available,
- Change in dietary factors.
- Exercise
- Weight loss
- Drugs
- Bariatric surgery (in women with massive obesity)
FERTILITY AFTER WEIGHT LOSS IN MEN AND WOMEN
Weight loss is extremely effective in resumption of fertility in obese women by
- Resumption of ovulation
- Better spontaneous conception rate
- Reduced abortion rate etc.
In obese men by
- Improving hormonal balance and sperm quality
- Improved erectile function.
- Enhanced semen parameters
- Increased testosterone levels
- Reduced risk of metabolic disorders etc,
CONCLUSION
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for improving fertility in both men and women. Excess body weight disrupts hormonal and other metabolic status of the body leading to irregular cycles in women and abnormal sperm factors in male. By adapting a balanced diet and engaging in physical activity can positively impact reproductive health. Moreover, weight management can help in overall wellbeing and increases the chance of having successful conception and a healthy baby.
If you are passionate about knowing more about infertility, various causes and management of infertility, enrol into Fellowship in reproductive medicine course which will equip you with a deeper understanding of the field. Our program will prepare future infertility specialists with knowledge and skills needed to be a competent practitioner, while you are working.
